Service Hotline
Service Hotline
TEL:+86-18637917090Email:export01@lygangxinglass.com
Service Hotline
TEL:+86-18637917090Preface
GB 15763 "Safety Glass for Building Applications" is currently divided into two parts:
--Part 1: Fireproof glass;
--Part 2: Tempered glass.
This part is the second part of GB 15763.
5 of this section. 5, 5. 6, 5. 7 is a mandatory clause, while other clauses are recommended clauses.
This section replaces the relevant provisions on tempered glass for curtain walls in GB/T 9963-1998 "Tempered Glass" and GB 17841-1999 "Tempered Glass and Semi Tempered Glass for Curtain Walls".
The main changes in this section compared to GB/T 9963-1998 are as follows:
--This part is a mandatory standard, and GB/T 9963-1998 is a recommended standard;
--Revised the methods and requirements for fragment testing;
--The rules for referencing documents have been revised to distinguish between dated and undated references (GB/T 9963-1998, Part 2);
--Added the classification of vertical tempered glass and horizontal tempered glass (section 3 of this section);
--Incorporated the requirements for surface stress and thermal shock resistance of tempered glass for curtain walls in GB 17841-1999, and modified the requirements for surface stress (GB 17841-1999's 5.4,1.5.4,3,6.4,6.6; this part's 5.8,11,1,6.8,6.9);
--Added size requirements for glass circular holes (section 5.1.5 of this section);
--Revised the requirements for appearance quality;
--Removed methods and requirements for transmittance and wind pressure resistance performance;
--Revised sampling rules;
--Added explanation of stress spots and self explosion phenomena in tempered glass (Appendix A of this section).
Appendix A of this section is informative.
This section is proposed by the National Association of Architectural Glass and Industrial Glass.
This part is under the jurisdiction of the National Technical Committee for Standardization of Building Glass.
The drafting units responsible for this section include the Glass Science Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Building Materials Science, the Qinhuangdao Glass Industry Design and Research Institute, and the Building Materials Industry Technology Supervision and Research Center.
The drafting units participating in this part include Shenzhen South Glass Engineering Glass Co., Ltd., Guangdong Jingang Glass Technology Co., Ltd., Ningbo Jianghua Xinyi Safety Glass Co., Ltd., and Wuxi Xinhui Glass Products Co., Ltd.
The main drafters of this section are Yang Jianjun, Qiu Guohong, Han Song, Mo Jiao, Gong Shuyi, Wang Rui, Liu Zhifu, Li Jinping, Zhu Mei, Ai Fazhi, Wu Dehua, Zhuang Dajian, and Xia Weiwen.
The previous releases of standards replaced by this section include JC 293-82 "Flat Tempered Glass", GB 9963-88 "Tempered Glass", and GB/T 9963-1998 "Tempered Glass"; The section on tempered glass for curtain walls in GB 17841-1999 "Tempered glass and semi tempered glass for curtain walls".
Safety glass for building use - Part 2: Tempered glass
Safety glazing materials in building Part 2: Tempered glass
1 Scope
This part of GB15763 specifies the classification, technical requirements, test methods, and inspection rules of tempered glass for construction made by heat treatment process.
This part of GB15763 is applicable to tempered glass for construction made by heat treatment process. For tempered glass used outside of buildings (such as industrial equipment, furniture, etc.), if there is no corresponding product standard, this standard can be used according to its product characteristics.
2 2 Normative References
The clauses in the following documents become the clauses of this section through reference in this section. For dated reference documents, all subsequent amendments (excluding corrected content) or revisions are not applicable to this standard. However, parties to agreements based on this section are encouraged to study whether the latest versions of these documents can be used. For undated references, the latest version applies to this section.
GB 9962-1999 Laminated Glass
GB 11614 Float Glass
GB/T 18144 Glass Stress Testing Method
3 Definition and classification
3. 1 Definition
Tempered glass: Glass that has undergone heat treatment. Its characteristic is the formation of a compressive stress layer on the surface of the glass, which improves its mechanical strength and thermal impact strength, and has a special fragmentation state.
3. 2 Classification
3. 2. Tempered glass can be classified into:
Vertical tempered glass: Tempered glass produced by hanging with clamps during the tempering process.
Horizontal tempered glass: Tempered glass produced by horizontal roller support during the tempering process.
3. 2. Tempered glass is classified into flat tempered glass and curved tempered glass according to its shape.
Glass used for tempered glass
The quality of the glass used in the production of tempered glass should meet the requirements of the corresponding product standards. For glass with special requirements for the production of tempered glass, the quality of the glass shall be determined by both the supply and demand parties.
5 Requirements
The various properties and testing methods of tempered glass should comply with the corresponding provisions in Table 1. The safety performance requirements are mandatory.
Table 1 Technical Requirements and Test Method Terms
5.1 Permissible dimensions and deviations
5.1.1 Allowable deviation of side length of rectangular flat tempered glass
The allowable deviation of the side length of rectangular flat tempered glass should comply with the provisions of Table 2
Table 2 Allowable Deviation of Edge Length of Rectangular Flat Tempered Glass (Unit: Millimeters)

Figure 4 Representation method of center position
5.2 Thickness and its allowable deviation
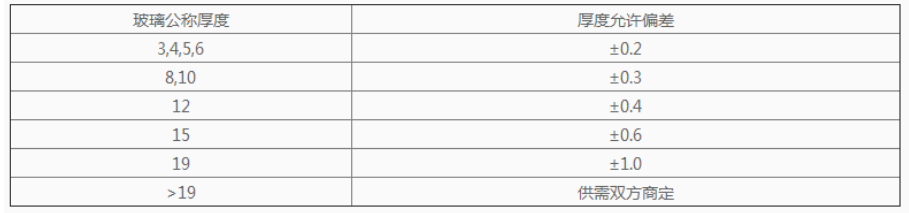
5.2.1 The allowable deviation of the thickness of tempered glass should comply with the provisions of Table 5.
Table 5 Thickness and its allowable deviation (in millimeters)
5.1.3 Dimensions and allowable deviations of tempered glass in other shapes
To be agreed upon by both the supply and demand parties.
5.1.4 Edge processing
The shape and quality of edge processing shall be agreed upon by both parties
5.1.5 Round hole
5.1.5.1 Overview
This clause only applies to tempered glass with a nominal thickness of not less than 4mm. The quality of edge processing of circular holes shall be agreed upon by both the supply and demand parties.
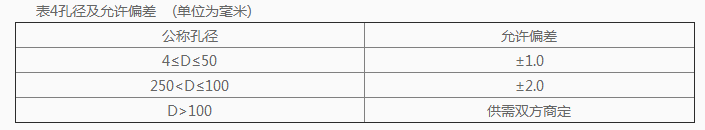
5.1.5.2 Aperture
The aperture is generally not less than the nominal thickness of the glass, and the allowable deviation of the aperture should comply with the provisions of Table 4. The allowable deviation for the aperture of holes smaller than the nominal thickness of glass shall be agreed upon by both parties,
Table 4 Aperture and allowable deviation (in millimeters)
5.1.5.3 Location of holes
1) The distance a between the edge of the hole and the edge of the glass should not be less than twice the nominal thickness of the glass. As shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the distance between the edge of the hole and the edge of the glass
2) The distance b between the edges of two holes should not be less than twice the nominal thickness of the glass. As shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the distance between the edges of two holes
3) The distance c between the edge of the hole and the corner of the glass should not be less than 6 times the nominal thickness d of the glass. As shown in Figure 3.
Note: If the distance between the edge of the hole and the corner of the glass is less than 35mm, then the hole should not be in a symmetrical position relative to the corner. The specific location shall be agreed upon by both the supply and demand parties.
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of the distance between the edge of the hole and the corner of the glass
4) Method for representing the position of the center of a circle and its allowable deviation
The expression method for the position of the center of a circular hole can refer to Figure 4. Establish a coordinate system as shown in Figure 4, and use the position coordinates (x, y) of the center of the circle to express its position.
The allowable deviation of the position x and y of the center of the circular hole is the same as the allowable deviation of the glass edge length (see Table 2).
Figure 4 Representation method of center position
5.2 Thickness and its allowable deviation
5.2.1 The allowable deviation of the thickness of tempered glass should comply with the provisions of Table 5.
Table 5 Thickness and its allowable deviation (in millimeters)
5.2.2 For glass with nominal thickness not specified in Table 5, the allowable deviation in thickness can be determined by the provisions of Table 5 for glass with thinner thickness adjacent to it, or by mutual agreement between the supply and demand parties.
5.3 Appearance quality
The appearance quality of tempered glass should meet the requirements of Table 6.
5.4 Bending
The curvature of flat tempered glass should not exceed 0.3% for arched shapes and 0.2% for wavy shapes.
5.5 Impact resistance
Take 6 pieces of tempered glass for testing. If the number of damaged samples does not exceed 1, it is considered qualified, and if there are more than or equal to 3 pieces, it is considered unqualified.
When the number of damages is 2, another 6 samples must be taken for testing, and all samples must not be damaged to be considered qualified.
5.7 Shotget Impact Performance
Take 4 flat tempered glass samples for testing, and they must comply with any of the following provisions (1) or (2).
(1) When glass is broken, the total mass of the maximum 10 fragments per sample shall not exceed a mass equivalent to an area of 65m2 of the sample.
(2) When the drop height of the shotgun bag is 1200mm, the sample is not damaged.
5.8 Surface stress
The surface stress of tempered glass should not be less than 90MPa.
Using the product as the sample, take 3 samples for testing. If all meet the requirements, it is considered qualified. If 2 samples do not meet the requirements, it is considered unqualified. If 2 samples meet the requirements, add 3 more samples. If all 3 samples meet the requirements, it is considered qualified.
5.9 Tempered glass with thermal shock resistance should withstand a temperature difference of 200 ℃ without damage.
Take 4 samples for testing, and when all 4 samples meet the requirements, the performance is considered qualified. When two or more pieces do not meet the requirements, it is considered unqualified. When one sample does not meet the requirements, add another sample. If it meets the requirements, the performance is considered qualified. When there are 2 samples that do not meet the requirements, add 4 new samples. If all of them meet the requirements, it is considered qualified.
6. Test method
6.1 Dimensional inspection
Measure the dimensions with a steel ruler or tape measure with a minimum graduation of 1mm
6.2 Thickness inspection
Measure at the midpoint of the four sides within 15mm from the edge of the glass plate using an outer diameter micrometer or an instrument of equivalent accuracy. The arithmetic mean of the measurement results is the thickness value. And rounded to 2 decimal places in millimeters (mm).
6.3 Appearance inspection
Using the product as the sample, proceed according to GB 11614 method.
6.4 Bending measurement
Place the sample at room temperature for more than 4 hours, place it vertically during measurement, and place 2 cushion blocks 1/4 below its long edge. Use a straight ruler or metal wire to horizontally adhere to the two sides or diagonal direction of the product, measure the gap between the straight edge and the glass with a feeler gauge, and represent the curvature of the bow shape as a percentage of the ratio of the height of the arc to the length of the chord. When conducting local waveform measurement, use a straight ruler or metal wire to measure along the 25mm direction parallel to the glass edge, with a measurement length of 300mm. Measure the height of the trough or peak using a feeler gauge and divide it by 300mm to represent the curvature of the waveform as a percentage, as shown in Figure 6.
6.5 Impact resistance test
6.5.1 The sample is of the same thickness and type as the product, and the size manufactured under the same process conditions as the product is 610 mm (-0mm,+5mm) × 610mm (-0mm,+5mm) flat tempered glass.
6.5.2 The testing device should comply with the provisions of Appendix A of GB 9962-1999. Keep the impact surface level. When testing curved tempered glass, corresponding auxiliary frames need to be used for support.
6.5.3 Use a smooth surface steel ball with a diameter of 63.5 mm (mass of approximately 1040 g) and place it at a height of 1000 mm from the surface of the specimen, allowing it to fall freely. The impact point should be within a range of 25 mm from the center of the specimen. Impact each sample only once to observe if it is damaged. The experiment was conducted at room temperature.
6.6 Fragment state test
6.6.1 Using the product as the sample
6.6.2 Test equipment
Any device that can retain fragmented patterns.
6.6.3 Test steps
6.6.3.1 Place the tempered glass sample freely flat on the test bench and use transparent tape or other means to constrain the glass periphery to prevent glass fragments from splashing.
6.6.3.2 Impact the specimen with a small hammer or punch with a tip curvature radius of 0.2mm+0.05mm at a distance of about 20mm from the periphery on the centerline of the longest edge of the specimen, causing the specimen to break.
6.6.3.3 The measures to retain the pattern of fragments should start 10 seconds after impact and end within 3 minutes after impact.
1. Bow deformation
2. Glass edge length or diagonal length
3. Waveform deformation;
4. 300mm
Figure 6 Schematic diagram of bow and waveform curvature
6.6.3.4 When counting fragments, the parts within a radius of 80mm from the impact point and 25mm from the glass edge or drilling edge should be removed. Select the part with the largest fragment from the pattern, and use 50mm in this part × A 50mm counting box is used to calculate the number of fragments within the box, and no penetrating cracks are allowed within each fragment. Fragments that span the edge of the counting box are calculated as 1/2 fragments.
6.7 Impact performance test of loose ammunition bags
6.7.1 Sample
The sample is 1930mm (-0mm,+5mm) in size, with the same thickness as the product and manufactured under the same process conditions as the product × 864mm (-0mm,+5mm) rectangular flat tempered glass.
6.7.2 Test equipment
The testing device should comply with the provisions of Appendix B of GB 9962-1999.
6.7.3 Test steps
6.7.3.1 Use a flexible steel wire rope with a diameter of 3 mm to lift the impact body, so that the outer circumference of the maximum diameter section of the impact body is less than 13 mm from the surface of the sample and within 50 mm from the center of the sample.
6.7.3.2 Maintain the center position of the maximum diameter of the impact body at a drop height of 300 mm, freely swing and fall, and impact the specimen near the center point once. If the sample is not damaged, raise it to 750 mm and impact it again near the center point of the same sample.
6.7.3.3 When the specimen is still undamaged, raise it to a height of 1200 mm and impact it once near the center point of the same specimen.
6.7.3.4 When the sample with a drop height of 300mm, 750mm or 1200mm is damaged, within 5 minutes after the failure, select the largest 10 pieces from the glass fragments and weigh their mass. And measure the length of the longest glass fragment retained in the frame without penetrating cracks.
6.8 Surface stress measurement
6.8.1 The sample is made from the product and tested according to the method specified in GB/T 18144.
6.8.2 Regulations on measurement points
As shown in Figure 7, at a distance of 100mm from the long side, two parallel lines are drawn parallel to the long side and intersect with the diagonal at four points. These four points, along with the geometric center point of the product, are the measurement points.
Figure 7 Schematic diagram of measurement points
Figure 8 Schematic diagram of measurement points
If the length of the short edge of the product is less than 300mm, as shown in Figure 8, two parallel lines parallel to the short edge and the centerline intersect at 2 points at a distance of 100mm from the short edge. These two points, as well as the geometric center point of the product, are the measurement points.
The stress measurement points for irregularly shaped products shall be agreed upon by both the supply and demand parties.
6.8.3 Measurement results
The measurement result is the arithmetic mean of the measurement values at each measurement point.
6.9 Heat resistance and impact performance will be improved by 300mm × A 300mm tempered glass sample is placed in an oven at 200 ℃± 2 ℃ for at least 4 hours. After removal, the sample is immediately vertically immersed in a 0 ℃ ice water mixture, ensuring that more than one-third of the sample height can be immersed in water. After 5 minutes, observe if the glass is damaged.
Fish scale like peeling on the surface and edges of the glass should not be considered as damage.
7 Inspection Rules
7.1 Inspection items
Inspection is divided into factory inspection and type inspection.
7.1.1 The safety performance requirements in the technical requirements for type inspection are mandatory items, and the remaining requirements are agreed upon by both the supply and demand parties.
7.1.2 Factory inspection thickness and its deviation, appearance quality, size and its deviation, and curvature. Other inspection items shall be agreed upon by both parties.
7.2 Batch sampling method
7.2.1 The size and deviation, appearance quality, and curvature of the product shall be randomly sampled according to Table 8.
Table 8 Sampling Table (Unit: Pieces)

7.2.2 For other technical performance requirements of the product, if using product inspection, randomly select from the batch of products according to the quantity required by the testing items; If samples are used for inspection, samples prepared under the same process conditions should be used. When the batch of products exceeds 500 pieces, samples are taken in batches for every 500 pieces. When the inspection item is non-destructive testing, it can be used to continue testing other items.
7.3 Judgment rules
If the number of non-conforming products is equal to or greater than the non-conforming judgment number in Table 8, it is considered that the appearance quality, dimensional deviation, and curvature of the batch of products are unqualified.
Other performance should also comply with the provisions of the corresponding clauses, otherwise, the item is considered unqualified.
If one of the above items is unqualified, it is considered that the batch of products is unqualified.
8 Marking, Packaging, Transportation, and Storage
8.1 Packaging
The packaging of glass should be in wooden boxes or containers (racks), which should be easy to load, unload, and transport. Each box (rack) should be filled with glass of the same thickness and size. Protective measures should be taken between glass and glass, as well as between glass and boxes (racks), to prevent glass damage and scratches on the glass surface.
8.2 Packaging Marks
The packaging label should comply with the relevant national standards, and each packaging box should be marked with signs or words such as "facing up, handling with care, being careful of breakage, and being protected from rain and moisture".
8.3 Transportation
During transportation, the glass should be firmly fixed to prevent sliding and tipping, and there should be rainproof measures.
8.4 Storage
The product should be stored in a place without condensation or with rainproof facilities.


Whatsapp Scanning
Luoyang GangXin Glass Technology Co.,Ltd
Add: No.246, Jinshui Avenue, Airport Industrial Zone, Luoyang, Henan Province China
Tel: +86-186 3791 7090
Fax: +86-379-62201609
E-Mail: export01@lygangxinglass.com
Oversea Sales Manager: Tracy Liu
Email: export01@lygangxinglass.com
Mob/Whatsapp: +86-186 3791 7090
Oversea Sales: Michael Sun
Email: sales01@lygangxinglass.com
Mob/Whatsapp:+86-186 3848 1875
© 2021-2023 Luoyang GangXin Glass Technology Co.,Ltd all rights reserved 豫ICP备11020387号-1丨营业执照 Technical support: Glacn.cn

